cremasteric reflex test testicular torsion|testicular torsion prognosis : tv shopping Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. A thorough history, the presence of a painful .
8 de nov. de 2022 · O Avaí soma 29 pontos, tem sete vitórias, oito empates e 21 derrotas. O Juventude está na lanterna com 21 pontos. Os dois times já estão matematicamente .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web11 de set. de 2021 · Crystal Palace: Guaita; Ward, Andersen, Guehi, Mitchell; McArthur, Kouyaté, Gallagher; Ayew, Benteke, Zaha. Técnico: Patrick Vieira Tottenham: Lloris; .
Another way to diagnose testicular torsion is by checking for the cremasteric reflex by pinching or stroking the inner thigh on the affected side. Normally, this reflex causes the testicle to contract and rise, but it is often .Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding . Definition: Twisting of the spermatic cord leading to decreased blood flow to the testicle resulting in ischemia, infarction and potentially, tissue necrosis. Epidemiology: Most .The reflex may be absent in both UMN and LMN lesions. Children might show an exaggerated response to the reflex. Recent abdominal surgery, scrotal pain, and testicular torsion may .
Additionally, the cremasteric reflex is unreliable in young patients, especially those under one year old. The Prehn sign is not reliable for predicting torsion (relief of pain .
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. A thorough history, the presence of a painful . The best predictors for torsion include vomiting, testicular swelling, a firm testicle, a high–riding testicle, and an absent cremasteric reflex. A torsed testicle is only viable for about 4–6 hours after the event.
The finding of an ipsilateral absent cremasteric reflex is the most accurate sign of testicular torsion. Torsion of the appendix testis is more common in children than testicular.Testicular torsion typically causes rapid onset of severe scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting, followed by scrotal edema and induration. Neither urinary frequency nor fever rules out testicular torsion, but the cremasteric reflex is usually absent.
testicular torsion signs on examination
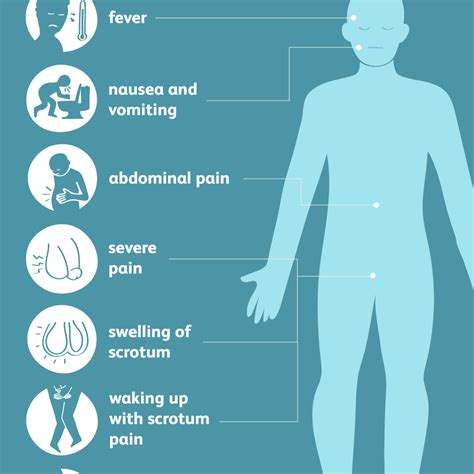
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of . Prehn’s test is used to differentiate testicular pain caused by acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. The test involves elevating the testes to assess the impact on testicular pain. A reduction in testicular pain is .Testicular torsion typically causes rapid onset of severe scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting, followed by scrotal edema and induration. Neither urinary frequency nor fever rules out testicular torsion, but the cremasteric reflex is usually .
Absent Cremasteric Reflex. The cremasteric reflex is elicited by lightly stroking the skin of the inner thigh. Normally, this causes the cremaster muscle to contract and elevate the testicle. Studies report varying sensitivities as low as 60%. The presence of a cremasteric reflex does not rule out torsion. Position of testis
Testicular Torsion: Diagnosis, Evaluation, . absent cremasteric reflex. If history and physical examination suggest torsion, immediate sur- . laboratory test results Hard mass within testicle .
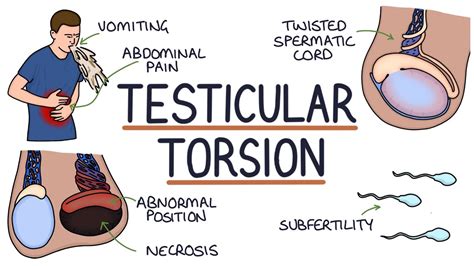
Create Personal Test Create Group Test . absent cremasteric reflex . Imaging. Doppler ultrasound . indications. if testicular torsion is suspected but not confirmed with physical exam and history. findings. decreased or absent blood flow. Studies. Urinalysis. to .An intact ipsilateral cremasteric reflex is frequently used, though imperfect, for excluding the diagnosis of testicular torsion. 12-14 This reflex is elicited by stroking the ipsilateral inner aspect of the thigh, which results in a reflexive elevation of the testicle through contraction of the cremaster muscle. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. . lie and maybe in a high position. The testicle may be swollen, erythematous, and have an absence of the normal cremasteric reflex; however, it should be noted that the presence or .Absent cremasteric reflex: 1 Nausea or vomiting: 1 High-riding testicle: 1 PPV 100% when >5 points (Suggesting stat urological consult) . ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of .
Sensitivity of cremasteric reflex in testicular torsion varies, ranging as low as 60% 6,7; . is the first-line imaging test recommended to rule in or out testicular torsion and should only be performed before surgical consult when patients with testicular pain have reassuring findings on history and exam. Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . clinical features (pain lasting less than 24 hours, nausea and/or vomiting, abnormal cremasteric reflex, and high position of the testis) were predictive with no false positives reported, thus .The cremasteric reflex is rarely intact in patients with testicular torsion but is usually present in patients with torsion of a testicular appendix. 2 A thorough testicular examination requires a . Test for the cremaster reflex. Used in patients with suspected cauda equina syndrome, in multiple sclerosis, testicular torsion, upper and lower motor neuron lesions, lesions at the level of L1/L2. The reflex also tests for the integrity of the ilioinguinal (sensory) nerve or the genitofemoral nerve (motor). To find out more about our work and the full range of our .
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. . there is a recognizable association between a hyperactive cremasteric reflex, . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that .Testicular torsion has an annual incidence of approximately 1 in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. 1 It is more common in children and adolescents, and delayed repair can result in the loss of .The significance of the cremasteric reflex in testicular torsion was reported by Rabinowitz1 in 1984. This report made the remarkable observation that the loss of the reflex is a 100% sensitive test for the presence of torsion. The specificity, .Studies show that the absent cremasteric reflex may have less than 90% sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing testicular torsion. 1,2,6,7 This large inconsistency makes it unsuitable as an adequate screening or diagnostic test .
Torsion of Testicular and Epididymal Appendages. The testicular appendix, also known as hydatid of Morgagni, and epidydimal appendix are remnants of embryological development.They can also twist to result in a torsion, presenting with unilateral scrotal pain and tenderness, however often with normal testicular lie and present cremasteric reflex.. On .
An absent cremasteric reflex is suggestive of testicular torsion (odds ratio = 7.8), whereas the reflex is preserved with epididymitis. 10 – 12 Torsion of the appendix testis is classically .
The cremasteric reflex is illicited by stroking/pinching the medial aspect of the thigh, causing a contraction of the cremasteric muscle, and elevation of the ipsilateral testicle at least 0.5cm. Studies show the absence of a cremasteric reflex has a less than 90% sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing testicular torsion.Absence of the cremasteric reflex is a characteristic of torsion in the pediatric population . A normal cremasteric reflex would result in elevation of the ipsilateral testis after an extra gentle stroke of the inner thigh. The cremasteric reflex is rarely seen in patients with testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a time sensitive, . Loss of cremasteric reflex. Previously thought to be 100% sensitive and highly specific; 30% of males with normal testicles will have an absent cremasteric reflex ; Studies report varying sensitivities as low as 60% (Mellick 2012)
The absence of the reflex is considered to be diagnostic for testicular torsion. The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. . demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion . The cremasteric reflex is fickle and may be absent in up to 30% of normal males without any pathology. Conversely, several case series report patients with surgically confirmed testicular torsion may still have preserved cremasteric reflexes anywhere from 8% .
Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours. . Classically, the cremasteric reflex is absent and pain continues despite elevation of the testicle, termed a negative Prehn’s sign . (if available, this test has a high sensitivity (89%) and specificity (99%)). Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). . Upon physical examination, the cremasteric reflex is absent. Normally, the cremasteric reflex can be triggered by stroking of the upper inner part of the thigh, which provokes .INDEX WORDS: Testicular torsion, cremaster, scrotum, re-flex. T HE CREMASTERIC REFLEX has been reported to be a useful sign in the diagnosis of testicular torsion.1,2 The normal reflex consists of cremasteric con-traction with elevation of the testis on stroking the medial thigh; the reflex is reported to be uniformly
Thermo gravimetric analyzer (TGA) exporting
Differential Thermal Analyzer exporting
WEB1 de set. de 2023 · Over e Under em outros esportes. A opção de apostar em over e under existe em quase todas as modalidades, sendo uma das principais o Basquete.. Neste esporte, você pode definir uma estratégia de quantos pontos combinados uma partida pode ter e apostar o seu palpite para mais ou menos de acordo com a linha oferecida pela .
cremasteric reflex test testicular torsion|testicular torsion prognosis